By Tom Bicknell, Fire Protection Association Australia
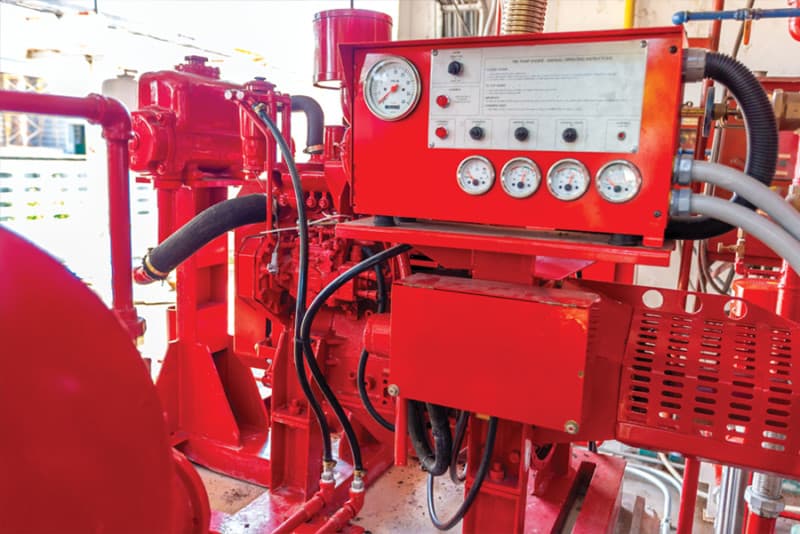
Pump sets are a critical part of fire hydrant and fire sprinklers systems. It is important to be aware of one of the key risks to this important equipment — battery failure. Through reports from its members, peak industry body Fire Protection Association Australia (FPA Australia) is aware of common faults with batteries supporting pump sets associated with fire protection systems.
The problem
The consistent fault reported has been that flooded-cell lead-acid batteries are ‘exploding’. This is thought to be a result of failure and rupture of the battery casing due to internal gas accumulation, and in some cases ignition of this gas.
Reported failures or ruptures are likely to be the result of incorrect charging of flooded-cell lead-acid automotive batteries that have been poorly maintained. Incorrect charging can cause electrolysis of the electrolyte fluid (sulphuric acid and water) that surrounds the lead plates within the battery. Electrolysis produces hydrogen and oxygen gases, and depletes the electrolyte of water.
While these types of batteries typically have vent holes to allow gases to escape the casing, these are insufficient to expel a high rate of gas production. Gas build-up can swell the casing, which may lead to ruptures and leakage of the fluid. Any spark associated with this build-up of gas will result in an explosion.
In the first instance, failure or rupture of the battery casing due to internal gas accumulation is a significant occupational health and safety issue. The corrosive substances contained within the battery casing are particularly harmful to clothing, skin and eyes and can be fatal if ingested. This is particularly concerning as typically there is no prior warning that failure or rupture is imminent when gases are ignited.
Such failures may also render the diesel fire pump set inoperable, which may also affect the performance of the fire hydrant or fire sprinkler system it serves.
The right battery
The prescriptive deemed-to-satisfy provisions of the Building Code of Australia, as referenced by federal, state and territory governments across Australia, require fire hydrant and sprinkler systems to be installed in accordance with the following standards:
AS 2419.1-2005, Fire hydrant installations – System design, installation and commissioning
AS 2118.1-2017, Automatic fire sprinkler systems – General systems
AS 2118.4-2012, Automatic fire sprinkler systems – Sprinkler protection for accommodation buildings not exceeding four storeys in height
AS 2118.6-2012, Automatic fire sprinkler systems – Combined sprinkler and hydrant systems in multi-storey buildings
All of these standards require fire compression-ignition (diesel) pump sets associated with these systems to be installed in accordance with AS 2941, Fixed fire protection installations – Pumpset systems, although the edition may vary.
The previous version of this Standard, AS 2941-2008, references a further standard which covered lead-acid batteries, AS 4029. Batteries which were compliant with AS 4029 were recommended as reducing the risk of explosion. Obtaining confirmation from battery manufacturers that their products had this compliance, however, was often difficult.
In the current version of the fire protection pump set standard, AS 2941-2013, the AS 4029 battery standard is not referenced, and instead focuses on the performance requirements for lead-acid batteries used in pump sets. These requirements, if met, will significantly reduce the risk of explosion.
FPA Australia also recommends the following steps to choose and maintain the battery correctly:
- The battery is correctly maintained
- The battery is of the Absorbed Glass Matt (AGM) type. These batteries do not require maintenance of the electrolyte fluid and are sealed except for the inclusion of a safety pressure relief valve to discharge gas build-up. The technology adopted by AGM batteries produces water as a by-product of the chemical reaction process. This means that there is no requirement to maintain electrolyte levels manually. This eliminates the identified risk of explosion that results from batteries drying out through depletion of electrolyte
- The correct float charge voltage is used. Float charge voltage is commonly recommended to be between 13.0 VDC and 13.8 VDC at 26.7°C; however, each manufacturer will have a specific charge voltage for their batteries. It is extremely important that the float charge voltage of the battery is set in accordance with the battery manufacturer’s requirements to prevent incorrect charging and gas build-up, which may result in an explosion risk.
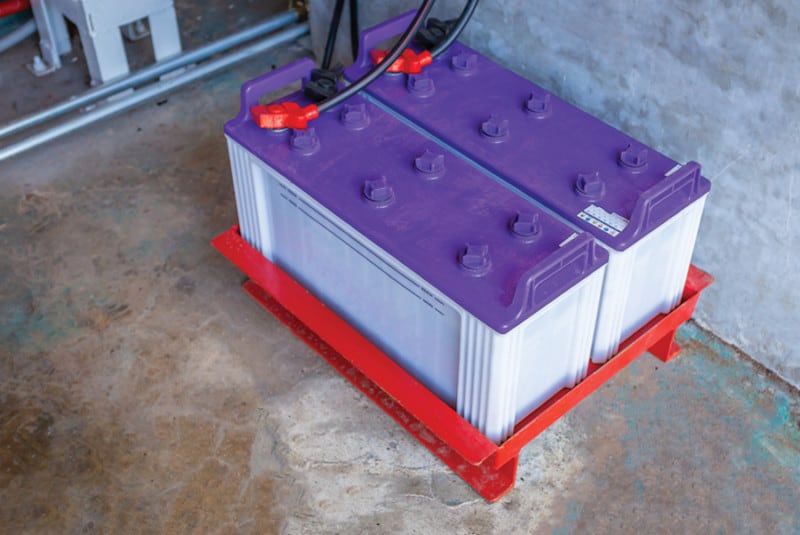

FPA Australia recommends the use of sealed absorbed glass matt (AGM) batteries in fire pumpsets.
The solution
FPA Australia recommends that stakeholders take the following steps to ensure the safety and integrity of batteries supporting fire pump sets:
- Wear eye protection and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when conducting maintenance
- Use additional caution at pump set start up (either manual start up or when automatic start up is expected after instigating pressure drop of fire protection systems)
- Observe OH&S rules that prevent the introduction of ignition sources within the proximity of batteries
- Where possible, determine that installed batteries comply with AS 4029.2. Where batteries have not been marked, check with the supplier of the batteries to ensure their compliance
- Batteries should be of the Absorbed Glass Matt (AGM) type, regardless of compliance with AS 4029.2, to reduce the likelihood of failure or explosion due to gas build-up caused by incorrect charging and depletion of electrolyte
- Always make sure the maintenance and the float charge voltage of the battery are in accordance with the manufacturer’s requirements
- Ensure that any documentation associated with installation of fire pump sets clearly specifies the use of batteries in accordance with recommendations 1 to 6 above. In particular, when replacing the battery, replace any flooded-cell lead-acid battery with an AGM type battery. This may require the charging voltage to be readjusted
- Where wet (flooded-cell) batteries with cell caps are fitted, check the electrolyte levels at each service or test before starting the diesel motor. If the electrolyte level is at or below the level of the plates, distilled water must be added before attempting to start the pump. A sufficient quantity of distilled water should be left where batteries are located at each site for battery top up
- Consider replacing existing batteries if the system’s original installation predates the AS 2941-2008 requirement or if the batteries are older than two years. Mark or record the date the battery was installed using an indelible marker or similar method
- Install appropriate warning signage